Arab AcademyCairo, Egypt
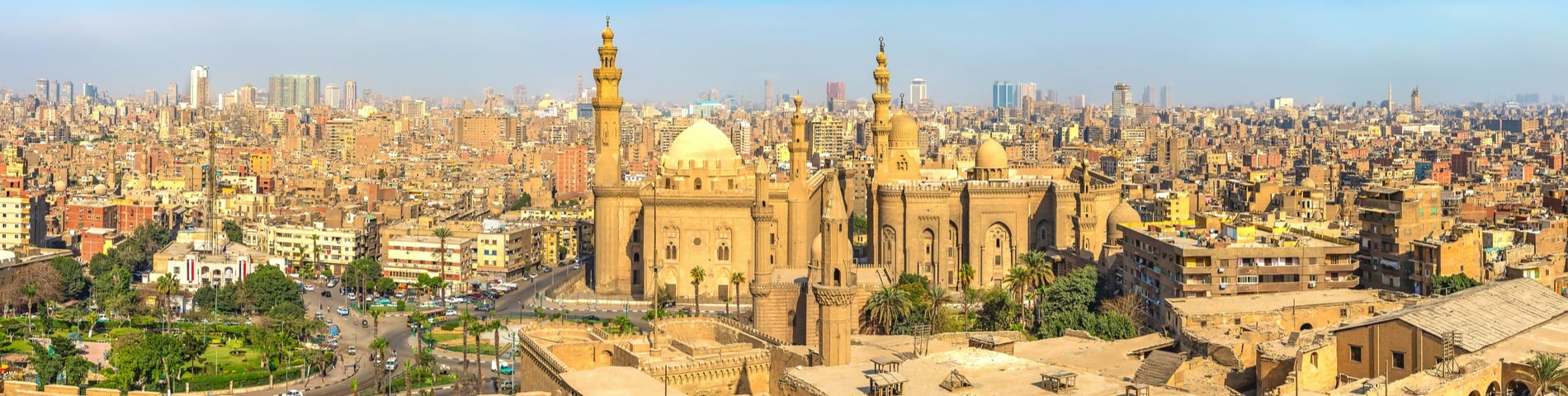
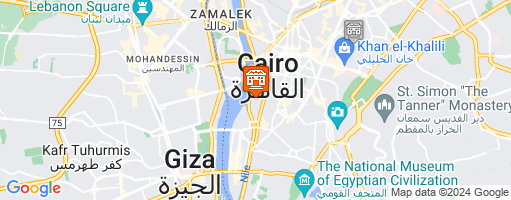
Location: Arab Academy is an Arabic language school located in Cairo, the capital city of Egypt. The school resides in the Garden City neighbourhood, which is an affluent part of the city.
Getting around: 10 minutes by foot from the school entrance is a ferry terminal for travelling down the River Nile. The Saad Zaghloul metro station is a short walk from Arab Academy, and this line stretches across the city. There are a number of bus stops near the school.
Social and Cultural: The public transport links around the school, reach main attractions such as the Mosque of Muhammad Ali and Khan el-Khalili. The Egyptian Museum and the Cairo Tower are walkable from Arab Academy.
Course selection: The school offers a range of Arabic programmes for classroom-based learning or through a virtual platform.
- The language school Arab Academy was founded in Cairo, Egypt in 1998.
- Tax registration ID: 239-813-863
Arabic Courses
Colloquial Arabic is the spoken Arabic used by Arabs in their everyday lives. Unlike MSA which is uniform in all Arab countries, colloquial Arabic is subject to regional variation, not only between different countries but also across regions in the same country. Arabic speakers from various parts of the world do communicate in their respective dialects. However, the degree and ease of comprehensibility depend on two factors:
- The geographical location pertaining to the dialects
- The level of exposure to each dialect.
This course is designed for students who know little or no Egyptian Arabic and those who need a refresher of the basics. It is recommended that students have a basic knowledge of Arabic before taking this course (Reading and writing of the Arabic Alphabet “Colloquial 100”). This basics course will cover daily life situations that a foreigner living in Egypt is likely to encounter. The course focuses on oral communication skills, listening skills and cultural skills which will be developed through situational discussions and dialogues.
Learning Outcomes
- Initiate social interactions, ask for basic information, and be aware of basic cultural aspects of social interaction in the Arab world.
- Talk about themselves, their education, and their family with native Arabic speakers.
- Understand and engage in simple conversations on familiar topics.
- Interact and communicate with Egyptians on the streets of Cairo on issues related to daily life.
- Initiate social interactions, ask for basic information, and be aware of basic cultural aspects of social interaction in the Arab world.
Morning: 9:00 - 13:00
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA), as its name indicates, is the modern counterpart of Classical Arabic. It is the official language of 22 Arab countries and it is used in the oral and written form on all formal occasions. The main difference between MSA and Classical Arabic lies in the vocabulary. MSA reflects the needs of contemporary expression whereas Classical Arabic reflects the needs of older styles.
Learning Outcomes
- Distinguish between the Arabic letters in their oral and written forms.
- Distinguish the shape of the letter when it comes in the beginning, middle or end of the word.
- Read simple 3-4 letter words.
- Write the letters correctly in the beginning, middle and end of the word.
- Learn some simple vocabulary related to everyday life.
Morning: 9:00 - 13:00
Afternoon: 13:00 - 17:00
Colloquial Arabic is the spoken Arabic used by Arabs in their everyday lives. Unlike MSA that is uniform in all Arab countries, colloquial Arabic is subject to regional variation, not only between different countries, but also across regions in the same country. Arabic speakers from various parts of the world do communicate in their respective dialects. However, the degree and ease of comprehensibility depends on two factors:
- The geographical location pertaining to the dialects
- The level of exposure to each dialect.
This course is designed for students who know little or no Egyptian Arabic and those who need a refresher of the basics. It is recommended that students have a basic knowledge of Arabic before taking this course (Reading and writing of the Arabic Alphabet “Colloquial 100”). This basics course will cover daily life situations that a foreigner living in Egypt is likely to encounter. The course focuses on oral communication skills, listening skills and cultural skills which will be developed through situational discussions and dialogues.
Learning Outcomes
- Initiate social interactions, ask for basic information, and be aware of basic cultural aspects of social interaction in the Arab world.
- Talk about themselves, their education, and their family with native Arabic speakers.
- Understand and engage in simple conversations on familiar topics.
- Interact and communicate with Egyptians on the streets of Cairo on issues related to daily life.
- Initiate social interactions, ask for basic information, and be aware of basic cultural aspects of social interaction in the Arab world.
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA), as its name indicates, is the modern counterpart of Classical Arabic. It is the official language of 22 Arab countries where it is used in the oral and written form on all formal occasions. The main difference between MSA and Classical Arabic lies in the vocabulary. MSA reflects the needs of contemporary expression whereas Classical Arabic reflects the needs of older styles.
Learning Outcomes
- Distinguish between the Arabic letters in their oral and written forms.
- Distinguish the shape of the letter when it comes in the beginning, middle or end of the word.
- Read simple 3-4 letter words.
- Write the letters correctly in the beginning, middle and end of the word.
- Learn some simple vocabulary related to everyday life.
This is a great way to learn Arabic online for kids between kindergarten and fifth grade.
It is based on short stories. Young learners begin by learning the alphabet and then learn to speak Arabic through situations that relate to their age. This is done by giving them stories and interesting puzzles that revolve around important topics such as: jobs, colours, numbers, food, outings, animals, etc.
The program is self-paced. Once students complete a level, they get moved to the next one.
Colloquial Arabic is the spoken Arabic used by Arabs in their everyday lives. Unlike MSA that is uniform in all Arab countries, colloquial Arabic is subject to regional variation, not only between different countries, but also across regions in the same country. Arabic speakers from various parts of the world do communicate in their respective dialects. However, the degree and ease of comprehensibility depends on two factors:
- The geographical location pertaining to the dialects
- The level of exposure to each dialect.
This course is designed for students who know little or no Egyptian Arabic and those who need a refresher of the basics. It is recommended that students have a basic knowledge of Arabic before taking this course (Reading and writing of the Arabic Alphabet “Colloquial 100”). This basics course will cover daily life situations that a foreigner living in Egypt is likely to encounter. The course focuses on oral communication skills, listening skills and cultural skills which will be developed through situational discussions and dialogues.
Learning Outcomes
- Initiate social interactions, ask for basic information, and be aware of basic cultural aspects of social interaction in the Arab world.
- Talk about themselves, their education, and their family with native Arabic speakers.
- Understand and engage in simple conversations on familiar topics.
- Interact and communicate with Egyptians on the streets of Cairo on issues related to daily life.
- Initiate social interactions, ask for basic information, and be aware of basic cultural aspects of social interaction in the Arab world.
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA), as its name indicates, is the modern counterpart of Classical Arabic. It is the official language of 22 Arab countries where it is used in the oral and written form on all formal occasions. The main difference between MSA and Classical Arabic lies in the vocabulary. MSA reflects the needs of contemporary expression whereas Classical Arabic reflects the needs of older styles.
Learning Outcomes
- Distinguish between the Arabic letters in their oral and written forms.
- Distinguish the shape of the letter when it comes in the beginning, middle or end of the word.
- Read simple 3-4 letter words.
- Write the letters correctly in the beginning, middle and end of the word.
- Learn some simple vocabulary related to everyday life.
Information for all courses offered by Arab Academy
Lessons needed per Arabic language level
Our price includes
- INCLUDED Wireless LAN zone at school
Arab Academy

General school facilities
Kitchen for student use
Microwave for student use
Fridge for student use
Free after-class access to language learning software
Student support desk
Free water dispenser
Free WIFI
Classroom equipment
TV in all classrooms
Electronic whiteboard in all classrooms
Air conditioning in all classrooms
Ample natural light in most classrooms
Number of classrooms: 11Paid parking (<500m)
Student Age / Nationality
Top student nationalities
Age of students
Visa Documents
Student Testimonial Videos
FAQ about Arab Academy, Cairo
- What is the number of students per class at Arab Academy?Depending on the chosen course, the maximum number of students at Arab Academy varies from 1 students (Online Kids Arabic Course) to 6 students (Full-Time Course - Modern Standard Arabic)
- What is the qualification of the teachers at Arab Academy?100% of teachers at Arab Academy hold a university degree. 100% hold a recognized language teaching certificate.
- Which countries are students of Arab Academy from?The highest Nationality percentage at Arab Academy comes from USA with a 40% representation, followed by students from England (30%) and Italy (8%).
- Arab Academy offers courses for which ages?Arab Academy offers courses from 0 years to 99. Average age is 25 during the summer and 25 for the rest of the year.