EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM IN CANADA
INTRODUCTION
Education in Canada varies widely according to the province, even though the basic structure of the education remains the same. All provinces provide a free elementary and secondary education ending with Grade 12 everywhere except in Quebec, where the elementary and secondary education lasts 11 years followed by two years at a publicly funded pre-university college, a CEGEP or General and Vocational College. Due to the complexity of the Canadian education system, we will offer a general overview of the educational system as it is in most Canadian provinces.
From 5 or 6 years of age and up to 16 or 18, depending on the Province, education in Canada is mandatory. Public education is available in English and French throughout the country, however, outside of the province of Quebec and a few regions in Ontario and New Brunswick, most public schools use English as their primary language. In the province of Quebec, education in French is compulsory with only a few exceptions.
PRIMARY/ELEMENTARY EDUCATION
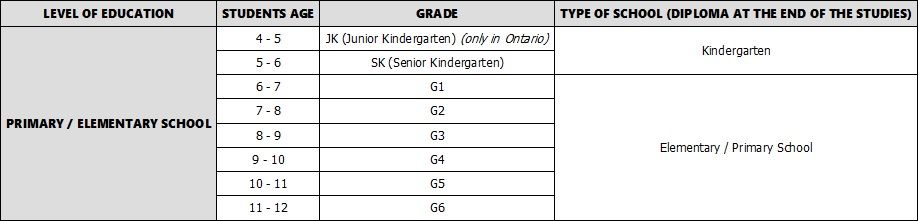
In most provinces, children start attending elementary school at age 5 with a year of Kindergarten. For the most part, this year is not mandatory. In some provinces, like Ontario, children can start Kindergarten one year earlier. This year of pre-Kindergarten is called "JK" or "Junior Kindergarten". After one or two years in Kindergarten, children begin their compulsory elementary education. Elementary school includes Grades 1 to 6 or 8, so from age 6 to age 12 or 14, depending on the province.
SECONDARY EDUCATION
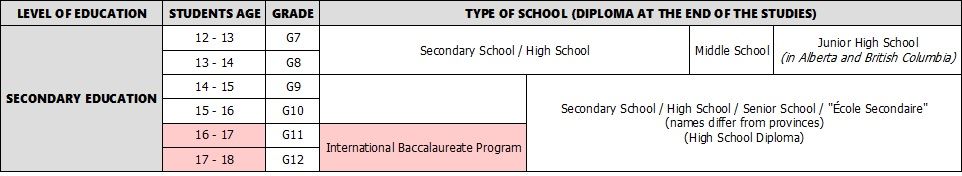
After elementary school, students start their secondary education, from Grade 7 or Grade 9 up to Grade 12 (ages 12/14 to 18). In some provinces, like Alberta and British Columbia, this means enrolling in a Middle School or Junior High School for 2 years before going to High School for another 4 years, while in other provinces high school lasts for the whole 6 years. In Ontario, what in many other places is part of secondary education, Grades 7 and 8, fall under the heading of elementary education and secondary education lasts only 4 years (Grades 9 through 12). High School has different names in different provinces. It can also be referred to as "Secondary School", "Senior School", or "Ecole Secondaire".
Secondary schools in Canada can be private, independent, or public (government-funded). Private secondary schools are often religious schools implementing a moral education and strict academic standards. Alternatively, they can be schools offering education in a different language, or following particular education methods or philosophies, or schools dedicated to specific areas of study, like the performing arts. Often private secondary schools have an international program in place to help foreign students adjust to the language and culture of their new surroundings.
At the end of their secondary education (Grade 12), students receive a High School or Secondary School Diploma, testifying the level they have reached during their 12 years of schooling. If students leave school before the end of their studies, they can later get a certificate equivalent to a high school diploma: the GED (General Education Development). This certificate attests that the student's knowledge and academic skills are on a par with those of a student who has completed secondary school. To obtain the certificate, students need to pass 5 tests in different subjects.
Preparation for University in high school: Advancement Placement Program:
The Advancement Placement Program is a secondary school program which provides courses at a university level in Canadian high schools, and also in the United States. These are courses at the level of a first year undergraduate university program and can give students credits toward their first year at university, essentially allowing them to skip an introductory course in a specific subject or go directly into an advanced course at university. The AP (Advancement Placement) exams aim at providing universities with information about a student's knowledge in a particular subject, skills and academic abilities, to decide if they are eligible for credit or not.
POST-SECONDARY EDUCATION
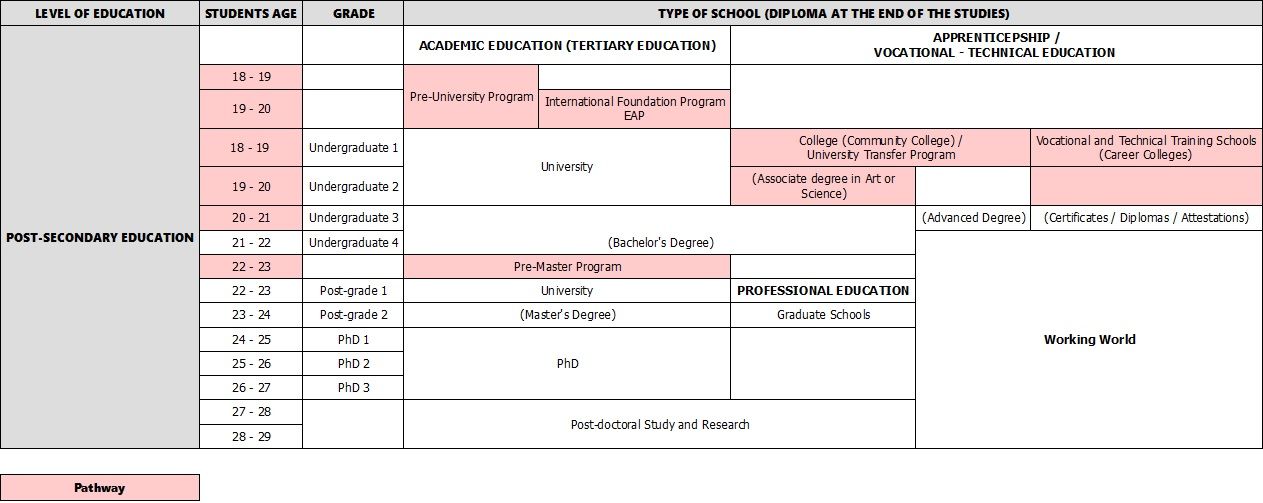
Each provincial and territorial government is responsible for its own post-secondary education in terms of establishing tuition fees and areas of study, but the general system remains the same. After high school, students can choose between following an academic path, through tertiary education (higher academic education) by going to a university, or to get ready for a specific career, through apprenticeship or vocational and technical training by attending a college. Tuition fees at public colleges and universities are lower than at the equivalent private institutions.
Tertiary Education (Higher Academic Education)
Pre-University Program:
For students who have decided to pursue an academic career, they have the option to take a pre-university program for 2 or 3 years, depending on their Major. This non-mandatory program gives them the necessary tools to enter the job market and to be ready to work. They also prepare them for the way of teaching at university, providing them with the academic skills required by Canadian universities.
In order to enter a Canadian university, students need to meet the criteria such as:
- having a high school diploma or equivalent with the corresponding academic transcripts
- having a language certificate attesting their level of French or English.
Pathways to University:
International students wishing to enter an undergraduate program in a university in Canada need to meet the university's expectations in terms of academic and language skills. They can take the International Baccalaureate Program that prepares them for the International Baccalaureate, an internationally recognized equivalent certificate for high school diplomas. They can also enroll in an International Foundation Program for 1 to 2 years before entering university to attain both the academic and English levels required to start an undergraduate program.
Bachelor's Degree:
Students can enter an Undergraduate program (Bachelor's Degree program) at university after completing a pre-university program or directly after high school. A pre-university program is specifically required in the fields of Business, Engineering, Computer Science, Nanotechnology, Nuclear Physics, Pharmacy, and Tourism. It takes 3 to 4 years to complete a Bachelor's Degree. In many universities, students have the option to take a "Double Major" combining two different disciplines, such as Chemistry and Biology to complete a Bachelor of Science in Chemistry and Biology.
After the completion of their undergraduate studies, students can continue their university studies by moving on to Master's Degree program, or can go to a Graduate School (Grad School).
Graduate/ Professional schools:
Graduate schools provide a more professional education. They are designed for students of professional fields like Law, Business, Medicine or Dentistry. Generally they require students to have completed a Bachelor's Degree, but some of them welcome students after only 2 or 3 years of an undergraduate program.
Pre-Master Program:
International students wishing to pursue their studies in Canada after having completing a Bachelor's Degree abroad can prepare for their Master's Degree by following the Graduate Pathway programs named Pre-Master Program ("Pre-Graduate Preparation"). This program usually last for 1 academic year and is intended to help students prepare for and adjust to the studying in English at a postgraduate level.
More information about the Pre-Master Programme
Master's Degree:
To start a Master's Degree, students generally must have completed an "Honours Degree", i.e. the fourth year of an undergraduate program. A Master's Degree deepens the student's knowledge acquired during his or her Bachelor's Degree program in the chosen field of study. It lasts 1 or 2 years, and leads to a Doctorate if the student wants to reach the final and highest academic level. As the student gains more skills in their specific field, it boosts their chances of finding a job in the marketplace. Students need to write a thesis or research paper to complete their Master's Degree.
Doctorate:
A Doctorate or PhD usually lasts 2 or 3 years and is the highest academic Degree that can be reached in tertiary education. Students generally choose to do a PhD after having completed a Master's Degree. In order to get the Degree, they need to write a thesis.
Vocational Education
Students who are not interested in an academic career can enroll in a college (community college) or in a vocational training school (career college). Colleges are more career-oriented, closer to the labour market than universities and offer vocational and technical programs that are consistent with changes in the industry and the job market and that meet employers expectations. They also provide pre-trades and apprenticeship training, as well as language training. There are many areas of study offered by vocational schools from Agriculture, Business, Health, Design, Social Sciences and Engineering, to Languages, Art, and Environment.
Community College:
Community colleges are part of the vocational education. They can either lead to an Associate Degree, or an Advanced Degree. The Associate Degree is reached after 2 years in a community college and is specifically for Arts and Science Degrees. Students get an Advanced Degree after 3 or 4 years in a community college. In some Provinces and areas of study, students can transfer from community college to university to finish their undergraduate study. It is called a University Transfer Program.
Community colleges present several advantages compared to universities. They have small classrooms, provide training courses as well as general subjects such as maths, English, science and psychology. They give students the option to go back to academic studies or to pursue a professional path, and have partnerships with professional organizations and employers, which can be a real asset for a student's future career.
Vocational training school (career college):
Vocational training schools are, usually private, institutions which focus even more on specific fields of study than community colleges and are clearly career-oriented. The preparation they provide is intended to allow students direct entry into the workforce after their studies.
LANGUAGE SCHOOLS
As an officially bilingual country, Canada disposes of two language programs (ESL and FSL: English as a Second Language and French as a Second Language) provided at different levels of education and by different institutions: middle schools, high schools, colleges, universities and language schools. Students can also follow an English for Academic Purposes (EAP) program. It is usually a 1 to 2-semester program and helps non-native English speakers who want to enter an English speaking university to reach the required level of English.